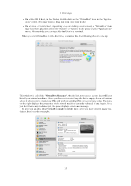
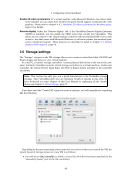
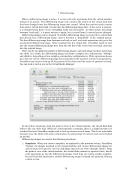
Glossary N NAT Network Address Translation. A technique to share networking interfaces by which an interface modifies the source and/or target IP addresses of network packets according to specific rules. Commonly employed by routers and firewalls to shield an internal network from the Internet, VirtualBox can use NAT to easily share a host’s physical networking hardware with its virtual machines. See chapter 6.3, Network Address Translation (NAT), page 85. O OVF Open Virtualization Format, a cross-platform industry standard to exchange virtual appli- ances between virtualization products see chapter 1.12, Importing and exporting virtual machines, page 26. P PAE Physical Address Extension. This allows accessing more than 4 GB of RAM even in 32-bit environments see chapter 3.3.2, “Advanced” tab, page 42. PIC See APIC. PXE Preboot Execution Environment, an industry standard for booting PC systems from remote network locations. It includes DHCP for IP configuration and TFTP for file transfer. Using UNDI, a hardware independent driver stack for accessing the network card from bootstrap code is available. R RDP Remote Desktop Protocol, a protocol developed by Microsoft as an extension to the ITU T.128 and T.124 video conferencing protocol. With RDP, a PC system can be controlled from a remote location using a network connection over which data is transferred in both directions. Typically graphics updates and audio are sent from the remote machine and keyboard and mouse input events are sent from the client. A VirtualBox extension package by Oracle provides VRDP, an enhanced implementation of the relevant standards which is largely compatible with Microsoft’s RDP implementation. See chapter 7.1, Remote display (VRDP support), page 90 for details. S SAS Serial Attached SCSI, an industry standard for hard disk interfaces. See chapter 5.1, Hard disk controllers: IDE, SATA (AHCI), SCSI, SAS, page 71. SATA Serial ATA, an industry standard for hard disk interfaces. See chapter 5.1, Hard disk controllers: IDE, SATA (AHCI), SCSI, SAS, page 71. SCSI Small Computer System Interface. An industry standard for data transfer between devices, especially for storage. See chapter 5.1, Hard disk controllers: IDE, SATA (AHCI), SCSI, SAS, page 71. 268
Purchased from Demo (abedemo.tizrapublisher.com) for the exclusive use of unknown. © 2026 Demo. Please report unauthorized use to pirate@tizra.com