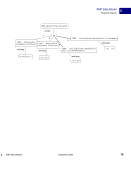
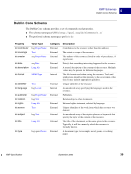
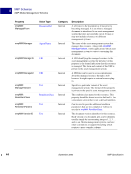
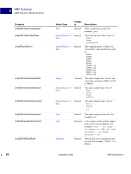
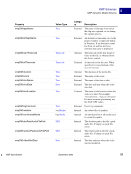
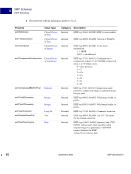
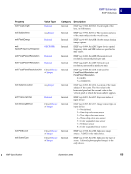
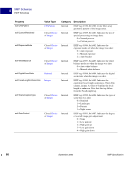
98 September 2005 XMP Specification Embedding XMP Metadata in Application Files HTML 5 HTML XMP embedded in HTML should conform to one of the W3C recommendations for embedding XML in HTML see Reference below. XML can be embedded in a SCRIPT or XML element, placed in any legal location the suggested location is the end of the HEAD element. The content of the SCRIPT or XML element is the XMP Packet. The browser must recognize the SCRIPT or XML element so that text representing the value of RDF properties is not displayed as page content. Using the XML element is preferred unless there are known incompatibilities with older software if so, the SCRIPT element is likely to be recognized. There are three approaches to embedding XML in HTML, as shown in the examples below. Two use the SCRIPT element, and the third uses the XML element. Using the SCRIPT element and LANGUAGE attribute html head SCRIPT LANGUAGE="XML" ?xpacket begin='' id='W5M0MpCehiHzreSzNTczkc9d'? !-- The serialized RDF goes here. It is removed for brevity. -- ?xpacket end='w'? /SCRIPT /head body /body /html NOTE: Adobe has noticed problems with using the SCRIPT element and LANGUAGE attribute in Microsoft Word 2000 running under Microsoft Windows XP: the body content cannot be displayed. Using the SCRIPT element and TYPE attribute html head SCRIPT TYPE="text/xml" ?xpacket begin='' id='W5M0MpCehiHzreSzNTczkc9d'? !-- The serialized RDF goes here. It is removed for brevity. -- ?xpacket end='w'? /SCRIPT /head body /body /html
Purchased from Demo (abedemo.tizrapublisher.com) for the exclusive use of unknown. © 2026 Demo. Please report unauthorized use to pirate@tizra.com