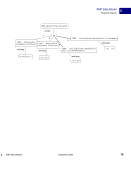
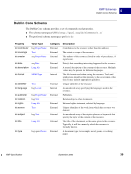
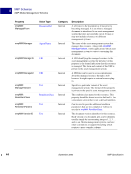
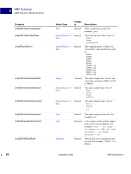
18 September 2005 XMP Specification XMP Data Model Property Values 2 Property qualifiers allow values to be extended without breaking existing usage. For example, the ns:role qualifier in the diagram does not interfere with readers who simply want the dc:creator names. An alternative would be to change dc:creator values to structures with name and role fields, but that would confuse old software that expected to find a simple value. The most common specific use of property qualifiers is for language alternative arrays (see next section). Language Alternatives Language alternatives allow the text value of a property to be chosen based on a desired language. Each item in a language alternative array is a simple text value, which must have a language qualifier associated with it. The language qualifier is a property qualifier, as described in the previous section. The qualifier name is xml:lang, and its value is a string that conforms to RFC 3066 notation. XMP uses the "x-default" language code to denote the default value for a language alternative. It should be the first item in the array, so that generic RDF processors will also use it as the default (according to the RDF default-is-first rule). The figure below shows an example: dc:creator "William Gilbert" "lyricist" ns:role Pirates of Penzance seq "Arthur Sullivan" "composer" ns:role 1 2
Purchased from Demo (abedemo.tizrapublisher.com) for the exclusive use of unknown. © 2026 Demo. Please report unauthorized use to pirate@tizra.com