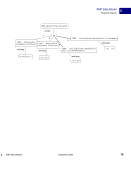
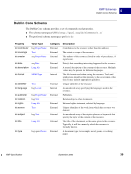
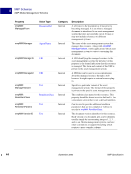
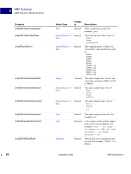
XMP Specification September 2005 111 Embedding XMP Metadata in Application Files PostScript and EPS 5 Object-Level Metadata Object-level XMP is written identically for PostScript and EPS. Metadata streams can be attached to specific objects in a PostScript file using the pdfmark operator. This is identical to the document-level PostScript method (see “Document-Level XMP in PostScript” on page 105), except that in step 3 the stream containing the XMP metadata is attached to the object. An example follows showing this for an image: % ====================================================================== % We assume that the XMP stream has been defined as shown earlier. All % but the third step, defining the stream as a metadata stream. We also % assume that the image has been defined as {myImage_123}. Again, a % unique name should be used. % % The third step is replaced with one that associates the XMP metadata % with the image. Since this must be located after both the image and % XMP streams, it might not be adjacent to the other XMP parts. See the % ordering issues discussed in “Ordering of Content”. % Third: Attach the XMP metadata stream to the image. [{myImage_123} /Metadata {my_metadata_stream_123} /PUT pdfmark NOTE: The approach shown here is compatible with all PostScript devices. That is, no additional changes are needed to ensure that level 1 devices will properly ignore the XMP beyond those already mentioned, and Distiller 5 and later will attach the XMP to the associated object in the PDF file. NOTE: Although Distiller 5 will attach the XMP to the associated object in the PDF file, the XMP stream in the PDF will be Flate-compressed. This makes the object XMP packet in the PDF invisible to external packet scanners. The XMP will be visible to software processing the PDF format and decompressing the stream. Distiller 6 and later do not compress the XMP packet stream.
Purchased from Demo (abedemo.tizrapublisher.com) for the exclusive use of unknown. © 2026 Demo. Please report unauthorized use to pirate@tizra.com